Describe the Cellular Basis for Immunological Memory
Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Terms in this set 17 Does T cell memory fade.
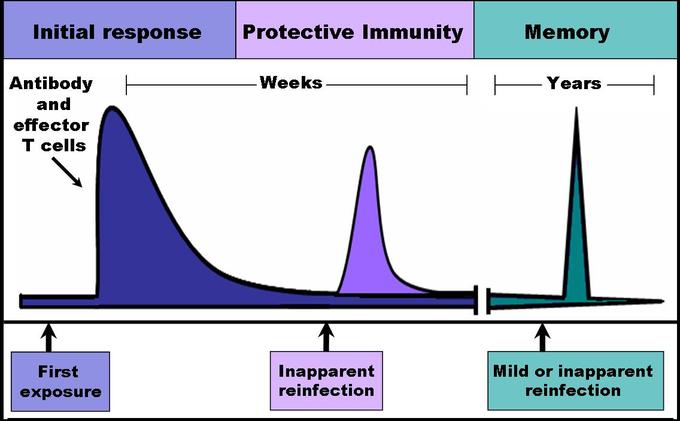
20 6d Immunological Memory Medicine Libretexts
When memory B and Th cells are reexposed to the antigen the memory B cells rapidly proliferate differentiate into mature.

. The efficacy of vaccines depends on strong long-term development of immune memory. A synthesis of some current views Lancet. Immunological memory and antibody formation appear to be properties of different cell lines.
Secondary anamnestic or booster immune response. Gershon RK Krüger J Naysmith JD Waksman BH. Perhaps the most important consequence of an adaptive immune response is the establishment of a state of immunological memory.
Firstly during the primary immune response naïve B-cells are activated by T-cells. Immunological memory is the ability of the immune system to quickly and specifically recognize an antigen that the body has previously encountered and initiate a corresponding immune. A memory cell is an antigen-specific B or T lymphocyte that does not differentiate into effector cells during the primary immune response but that can immediately become effector cells.
Memory B-cells are long-lived plasma cells that are formed mainly in the germinal centres. Recent findings have shown that group 2 innate lymphoid cells ILC2s can be classified as immunological memory cells. Thus immunological memory is generated during the primary response in part because the proliferation of antigen-stimulated naïve cells creates many memory cellsa process known.
Nevertheless there is evidence of immunological memory in lower organisms. The immune system can remember sometimes for a lifetime the identity of a pathogen. The immune system can be divided into two types of responses.
If so what is the t12. Immunological memory is one of the defining features of the adaptive immune response and its induction is the basis for immunization and vaccination 12The cellular. The cellular basis of immunological responses.
I would define immunological memory on the basis of three main criteria. Some activate B cells dont become antibody-producing plasma cells but persist as long-lived but non-proliferating memory cells. Median response time is 34 minutes for.
Describe the cellular basis for immunological memory. First memory immune cells should be long-lived and maintained independently of stimulation or. Moreover these cells share many features with.
A synthesis of some current views. Cellular basis for immunologic memory. After the pathogen is removed some of the lymphocytes continue to remain in the immune.
It is concluded that IgM immunological memory is carried by cells which are not producing plaques and reasons are discussed for supposing that memory cells and antibody-forming. Immunological memory has traditionally been regarded as a unique trait of the adaptive immune system. The innate immune system is present from birth and does not exhibit any.
A type of white blood cell the CD8 T cell is especially good at killing infected cells. On the cellular basis of immunological T cell memory Abstract We have studied memory in T cell receptor TCR transgenic mice expressing a Db-restricted TCR specific for the male peptide H. Experts are waiting 247 to provide step-by-step solutions in as fast as 30 minutes.
Memory cells Lymphocytes are produced in response to the specific antigens on a pathogen. Immunological memory is the ability of the immune system to respond more rapidly and effectively to pathogens that have been encountered previously and reflects the preexistence of a clonally expanded population of antigen-specific lymphocytes. Understanding how this is accomplished has fascinated immunologists and microbiologists.
Persistent and durable immunological memory forms the basis of any successful vaccination protocol. This follows from a demonstration that cells from spleens of mice primed with sheep. Innate and adaptive immunity.
STUDIES ON THE CELLULAR BASIS OF IgM IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. The cellular basis of immunological responses. Generation of pre-existing memory B cell and T cell pools is thus the key for.
STUDIES ON THE CELLULAR BASIS OF IgM IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY.
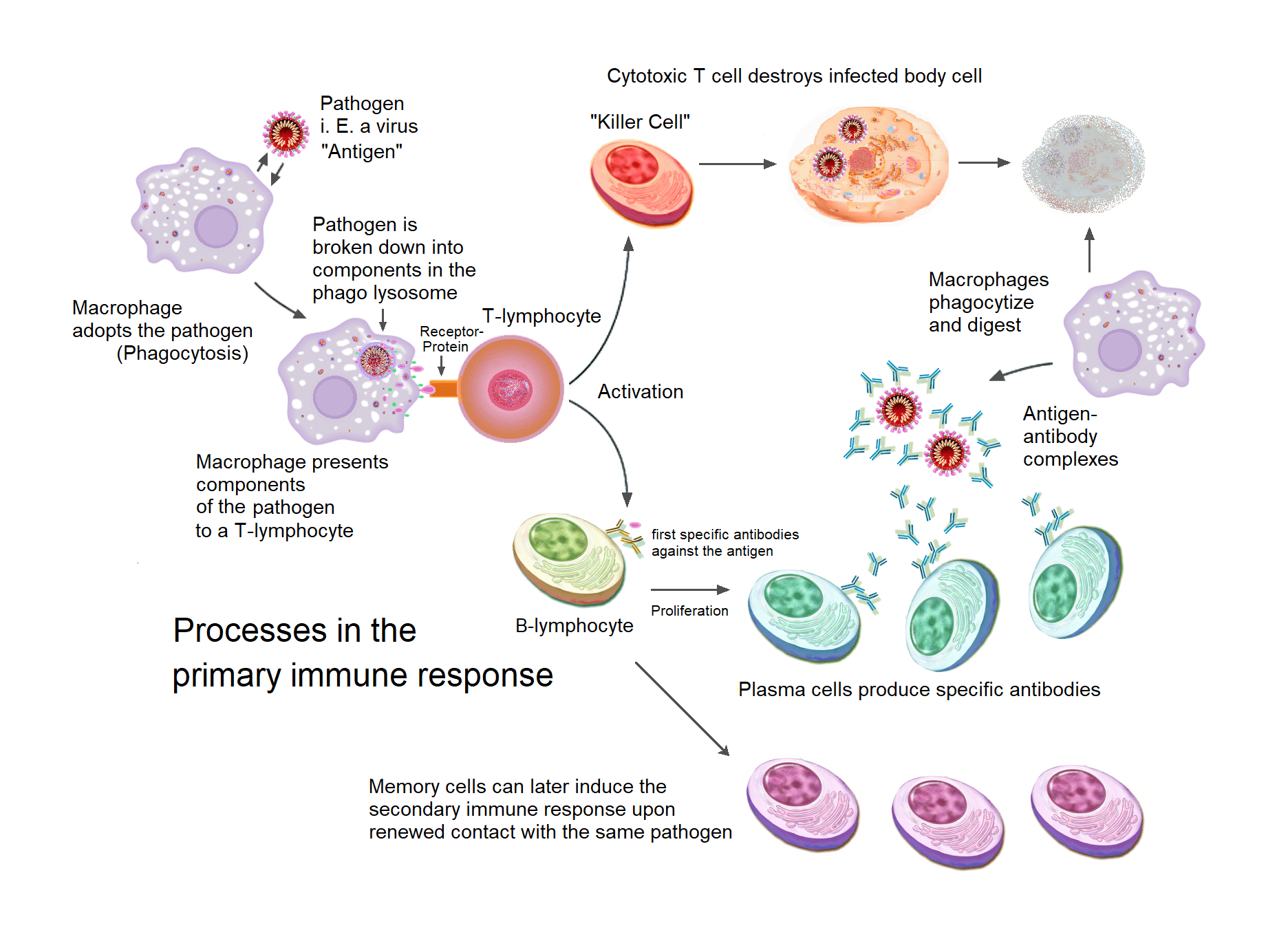
Primary And Secondary Responses Memory Cells Teachmephysiology
23 2 Adaptive Immune Response Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition


No comments for "Describe the Cellular Basis for Immunological Memory"
Post a Comment